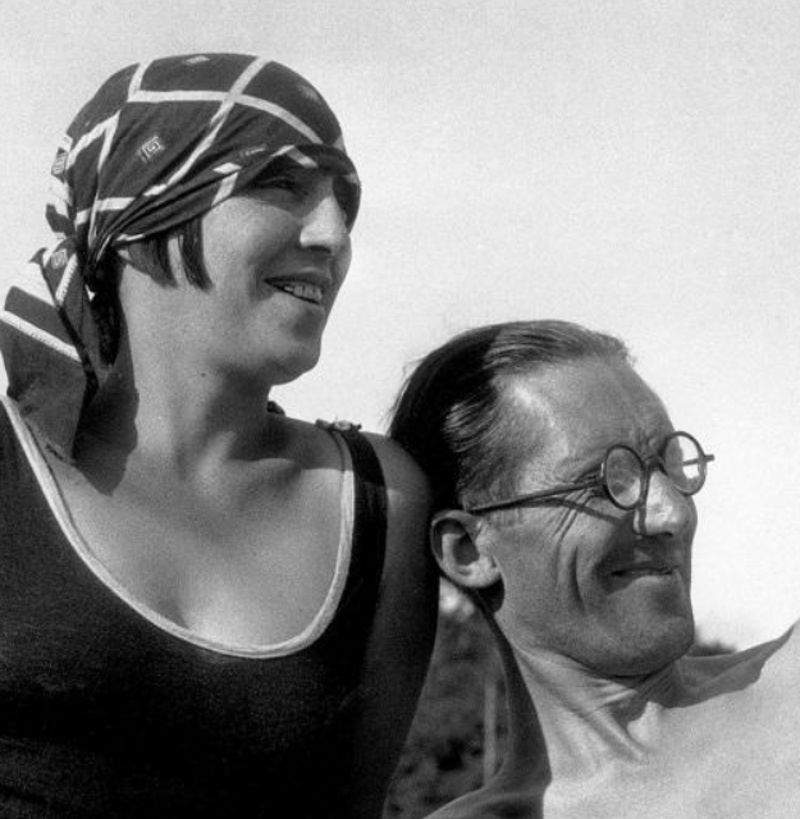Le Corbusier (1887-1965) was an architect, urban planner, and writer of Swiss-French origin. He is famous for his creations of buildings and master plans all over the globe, from France to Germany and from India to the United States and South America. Le Corbusier died of a heart attack while swimming on 27 August 1965 at the age of 77.
Contents
Wiki/Biography
‘Charles-Édouard Jeanneret,’ known as Le Corbusier was born on Thursday, 6 October 1887 (age 77 years; at the time of death) in La Chaux-de-Fonds city in Switzerland. He went to La-Chaux-de-Fonds Art School when he was fifteen. In 1902, he enrolled himself in a higher course of decoration. Le Corbusier never received formal training in architecture.
Family
Parents & Siblings
Le Corbusier’s father, Georges Edouard Jeanneret, was a watch engraver, and his mother, Marie Charlotte Amélie Jeanneret-Perret, was a piano teacher. Corbusier had an elder brother, Albert Jeanneret, who was a Swiss violinist.
Wife & Children
Le Corbusier got married to a former fashion model from Monaco, Yvonne Gallis, on 18 December 1930. The couple had no children. Yvonne died in 1957.
Relationships/Affairs
Le Corbusier had a long-time relationship with Swedish-American heiress Marguerite Tjader Harris even though he was married to Yvonne Gallis.
Signature/Autograph
Career
Architectural Innovation
Le Corbusier is known for his pioneering contribution to modern architecture. He embraced the principle of functionalism, emphasizing clean lines, open spaces, and the use of new materials. One of his iconic architectural works is Villa Savoye. [1]The New York Times
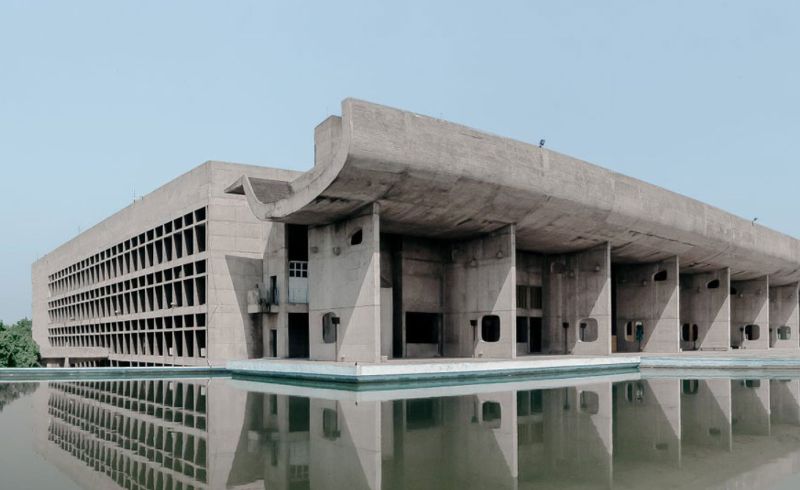
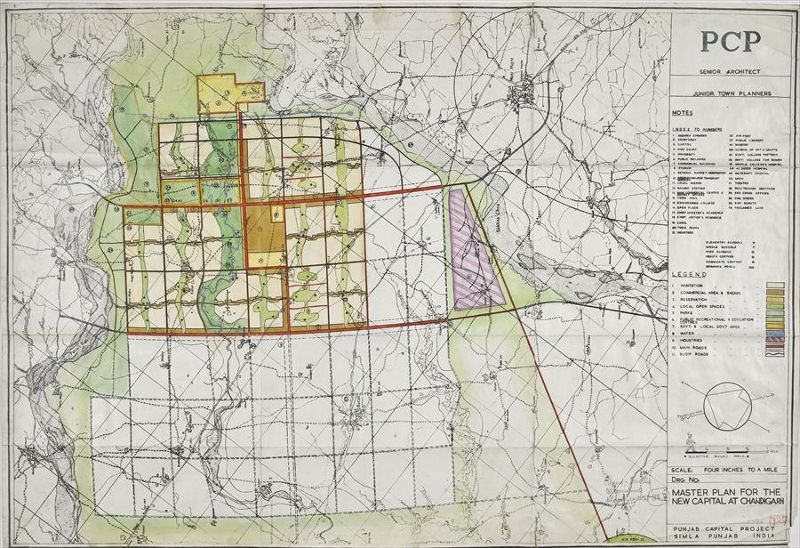
Master Plan of Chandigarh
Le Corbusier was involved with Albert Mayer and Maciej Nowicki in the design and planning of Chandigarh, a city in India. He was appointed as the chief architect for the project, which aimed to create a modern and organized city. He designed various government buildings including the Capitol Complex in the city. He also designed the master plan for Chandigarh. [2]The Indian Express
Architectural Based Books
Le Corbusier penned down his views in architectural-based books such as “Towards a New Architecture” and “The City Of Tomorrow and Its Planning,” which became influential texts in the field of architecture. He expressed his theories, ideas, and criticisms through his writings, contributing to architecture.
Urban Planning
Corbusier developed visionary urban planning concepts that aimed to address the challenges of rapid urbanization. His ideas revolved around functional zoning, high-rise buildings, and green areas. The Radiant City and the Plan Voisin for Paris were among his notable urban planning proposals.
International Influence
Le Corbusier’s impact extended beyond his native Switzerland and France. His ideas and designs influenced architects worldwide, and he played a significant role in shaping the modern architectural movement. His work left an imprint on urban landscapes and architectural education.
Controversies
Le Corbusier, the renowned architect, attracted controversies due to his urban planning ideas that often disregarded heritage, displaced communities, and lacked human scale. His collaboration with government authorities and the perceived social engineering in his designs also drew criticism. [3]The New York Times
Awards
- Le Corbusier was awarded a ‘Gold Medal’ from the ‘American Institute of Architects in 1961.
- He was honored with the title ‘Grand Officier of the Legion of Honour’ in 1964.
Death
On 27 August 1965, Le Corbusier died at the age of 77 due to a heart attack while swimming on the French Riviera in Roquebrune-Cap-Martin, France.
Facts/Trivia
- Before being an architect, Corbusier learned watch engraving and worked as a painter and decorator.
- Le Corbusier was born Charles-Édouard Jeanneret; however, in the 1920s, he changed his name to Le Corbusier.
- He also designed furniture such as sofas and chairs, which are even famous today.
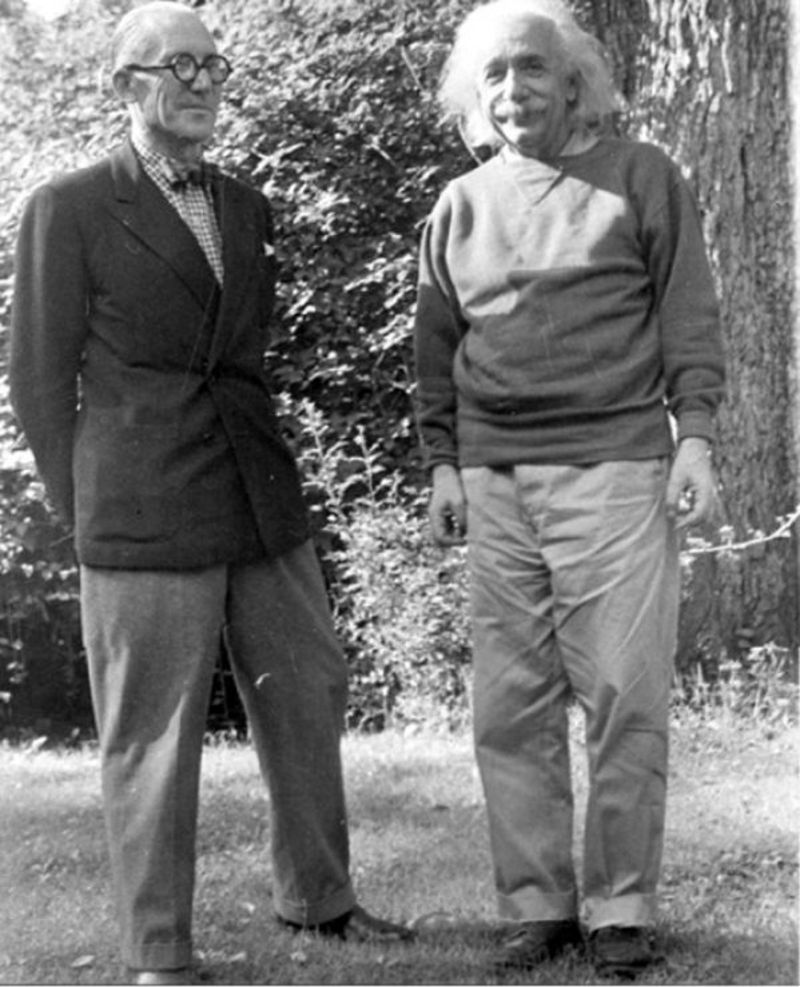
- Le Corbusier met with Albert Einstein at Princeton University in 1964 to discuss the “Modulor.”
- He loved maths and used mathematical principles in architectural designs.
- Le Corbusier didn’t have any formal architectural education rather he learned it all through practical experiments and self-study.
- After the death of Le Corbusier’s wife, Yvonne Gallis, he always kept her non-cremated bone with him as a sense of affection.
- Le Corbusier used to wear glasses and became blind in one eye by 1918.
References
| ↑1, ↑3 | The New York Times |
|---|---|
| ↑2 | The Indian Express |